How Solar Inverters Synchronize with the Grid A Seamless Connection
How Solar Inverters Synchronize with the Grid: A Seamless Connection
Understanding Solar Inverters
Solar inverters play a crucial role in the solar energy ecosystem. They are responsible for converting the direct current (DC) produced by solar panels into alternating current (AC), which is what most homes and businesses utilize. However, their function extends beyond mere energy conversion. One of their most vital roles is ensuring that the energy generated aligns perfectly with the existing electrical grid, enabling a seamless flow of electricity. This synchronization process is key to maximizing efficiency and maintaining grid stability.

The Synchronization Process
Synchronization involves matching the output of the solar inverter with the grid’s voltage, frequency, and phase. When a solar system is connected to the grid, the inverter continuously monitors these parameters. Any discrepancies between the inverter’s output and the grid are rapidly adjusted to ensure compatibility. This fine-tuning is essential not just for energy efficiency but also for safety, preventing situations that could lead to grid instability or damage.
Grid-Tied vs. Off-Grid Systems
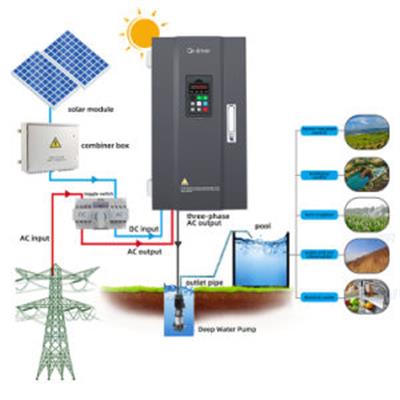
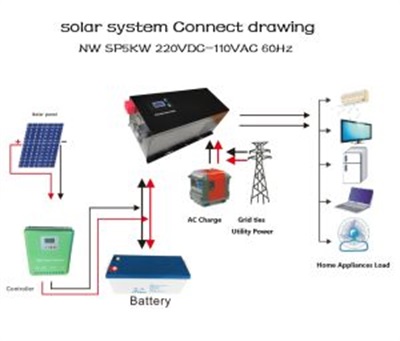
There are two primary types of solar systems: grid-tied and off-grid. Grid-tied systems are the most common and rely on synchronization with the electric grid. They can draw power from the grid when solar production is low and send excess energy back when production is high, thanks to net metering. On the other hand, off-grid systems are self-sufficient and use battery storage, making synchronization unnecessary. However, these systems require more complex management to ensure a consistent power supply.
Technological Innovations in Synchronization
Advancements in solar technology have significantly enhanced the ability of inverters to sync with the grid. Modern inverters are equipped with sophisticated software and hardware that allow them to perform rapid frequency and voltage adjustments. Many are also compliant with grid codes, which set standards for how renewable energy systems should interact with the grid. These innovations not only improve reliability but also foster greater integration of solar energy into the existing energy mix.
The Role of Smart Grids
The emergence of smart grid technology is revolutionizing how renewable energy sources, including solar, interact with traditional power systems. Smart grids use digital communication and sensors to monitor electricity flow and demand in real time. Solar inverters can communicate with the grid, adjusting their output based on real-time data. This dynamic interaction allows for more efficient energy distribution and enhances overall energy resilience, pushing towards a more sustainable future.

Challenges of Synchronization
Despite the advancements, there are still challenges in the synchronization of solar inverters with the grid. Variability in solar energy production due to weather conditions, for instance, can create fluctuations that inverters must manage. Additionally, as more homes adopt solar energy, the challenges of grid congestion and stability become more pronounced. Addressing these issues involves continuous innovation and collaboration between utility companies, technology developers, and regulatory bodies.
The Future of Solar Inverter Technology
The future of solar inverters looks promising, with ongoing research focused on improving efficiency and reliability. The trend towards more integrated energy systems is likely to continue, as governments and consumers alike push for cleaner energy solutions. As technology progresses, we can expect even smarter inverters capable of more precise synchronization with the grid, enabling a stronger and more resilient energy infrastructure.
Conclusion
Solar inverters are vital for connecting solar energy to the grid, ensuring a stable and efficient flow of electricity. As technology evolves, these devices will only become more adept at synchronizing with the grid, paving the way for a future powered by renewable energy. By understanding the intricacies of this synchronization process, we can appreciate the role solar inverters play in a more sustainable energy landscape.