Battery Packs BMS in Parallel Wiring
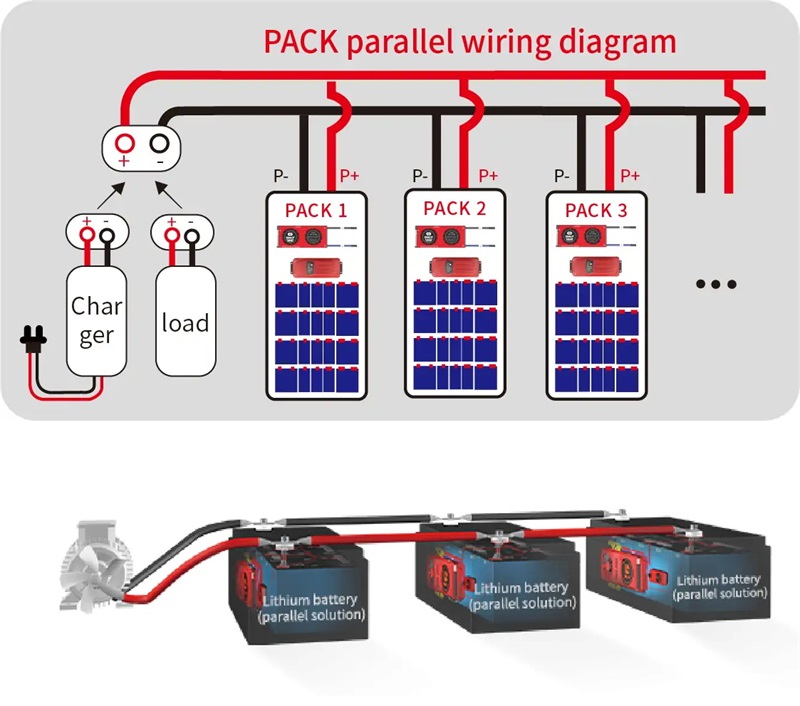
Parallel BMS (Battery Management System) is a management solution used when multiple battery cells are connected in parallel. Its main functions are to monitor parameters such as voltage and temperature, ensuring the safety and performance of the batteries. Below are detailed introductions to two common parallel BMS wiring methods.
Hybrid Series-Parallel Wiring Method
This method combines the advantages of both series and parallel connections, suitable for applications that require simultaneous management of multiple battery packs. The wiring involves connecting multiple battery packs in series, with the individual cells within each pack connected in parallel. The positive and negative terminals of each battery pack are connected to the corresponding ports on the BMS. The BMS monitors the total voltage and temperature of each battery pack, ensuring balanced charging and discharging across the packs. The advantages of this wiring method include its suitability for high-capacity battery systems, effectively increasing the overall voltage. Monitoring and management are more centralized, facilitating battery balancing. However, the complexity of the structure and the numerous connections can make maintenance challenging, requiring careful attention to the status of each battery pack.
Individual Cell Parallel Wiring Method
This method is suitable for small battery packs and is primarily used for connecting individual cells in parallel. The wiring involves connecting the positive and negative terminals of all individual cells to the corresponding ports on the BMS, forming a parallel circuit. The BMS ensures the status of each cell through internal current detection and voltage monitoring. The advantages of this method include a simple structure that is easy to implement and maintain. It allows for direct monitoring of each individual cell's status, facilitating battery balancing management. However, the drawback is that in high-capacity applications, it may lead to uneven loading among the individual cells, increasing the risk of battery damage.
Conclusion
When choosing the wiring method for a parallel BMS, decisions should be based on specific application scenarios, system requirements, and battery characteristics. The series-parallel mixed wiring method is suitable for high-voltage, large-capacity systems, while the parallel wiring method for individual batteries is better for smaller battery packs. Regardless of the chosen method, ensuring the safety and performance of the batteries is of utmost importance.

