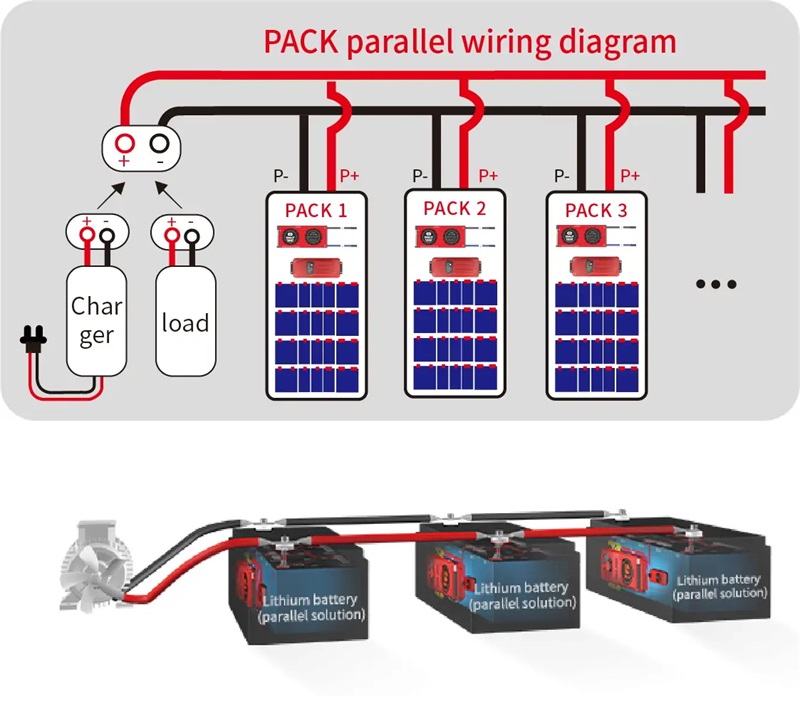
Analysis of Locomotive Battery: Driving the Power Core of the Future Railway

Locomotive batteries are crucial in locomotives and railway systems. It not only provides the initial energy needed to start the diesel engine, but also ensures stable operation in a variety of climatic conditions. The locomotive battery helps the locomotive overcome the challenge of oil thickening in cold weather, making the starting process smooth. In addition, the battery also supports the electronic system and safety equipment of the locomotive, guaranteeing the safety and efficiency of the entire railway transport. Without the support of the battery, the locomotive will not be able to exert its powerful power, and the normal operation of the railway system will be affected.
Main types of locomotive battery
There are currently different types of locomotive batteries that can be used in locomotives to take advantage of their unique advantages. Its types mainly include:
· Lead-acid battery: For many years, lead-acid battery locomotives have occupied an important position in the industry with their reliability and price advantages. Its simple design makes it an affordable option, while its durability allows it to withstand the harsh conditions faced by locomotives, including violent vibrations and extreme temperature changes.
· Lithium-ion battery: Lithium-ion batteries, on the other hand, have emerged as newer alternatives, with higher energy density and the ability to deliver more power despite their smaller size. This can reduce the weight of the locomotive and improve fuel efficiency. In addition, lithium-ion batteries discharge more slowly, so they can hold their charge for longer and do not need to be recharged frequently. In addition, they typically last longer compared to lead-acid batteries.
· Nickel metal hydride (NiMH) batteries: Another option for locomotives is the nickel-metal hydride battery (NiMH), which is a compromise between the two types of batteries mentioned above. Compared to lead-acid batteries, nickel-metal hydride batteries have a higher energy density and are a more compact solution.
Locomotive battery type analysis
We mentioned above that the battery products for railway locomotive batteries mainly include lead-acid batteries, nickel-cadmium batteries and lithium batteries. First of all, we make a simple comparative analysis of the product performance of railway locomotive batteries according to the battery capacity, charge and discharge life, safety and technical maturity:
In terms of battery capacity, lead-acid batteries: large capacity, suitable for high energy requirements, but relatively heavy. Nickel-cadmium batteries: smaller capacity, but can work stably under high loads. Lithium battery: high capacity, high energy density, lightweight, suitable for modern locomotive design; In terms of life, the lead-acid battery charge and discharge life is usually 500-1000 cycles, and the life is short. Nickel-cadmium batteries with approximately 1000 cycles are suitable for frequent charge-discharge applications. Lithium battery: up to 200 times or more, long cycle life, good economy; In terms of safety, lead-acid batteries may produce gas when charging, pay attention to ventilation. Nickel-cadmium batteries are relatively safe, but they contain heavy metals and need to be properly disposed of. Lithium batteries are safe under proper management, but they can cause fires if overcharged or damaged.
The upstream of batteries for railway locomotive batteries are mainly various raw materials, of which the upstream of lead-acid batteries are mainly lead and lead products (including lead, lead alloys, plates, terminals), plastics (PP materials, ABS materials, etc.) for the manufacture of battery shells, separators, grids, and other raw materials such as sulfuric acid; The upstream of cadmium-nickel batteries are mainly raw materials such as nickel powder and electrolyte. The upstream of lithium-ion batteries are mainly positive and negative electrode materials, electrolytes, electrode substrates, isolation films and tank materials.
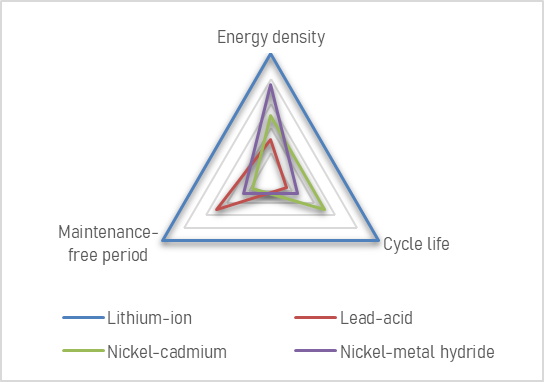
The use of many types of locomotive batteries brings a lot of benefits at the same time, followed by serious environmental pollution problems. Because the electrolyte or lead material of the lead-acid battery is not only very serious environmental pollution but also very serious harm to the human body. Therefore, under large-scale use, the development of the future society is not worth the loss. Then research and development to find alternative new energy batteries has become an important issue, and in terms of the current new energy batteries, only lithium batteries are promising, of which lithium iron phosphate batteries are most suitable for replacing lead-acid batteries.
Compared with lead-acid batteries, lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries have always had a wide range of application scenarios, stable battery performance, and its manufacturing materials are composed of non-toxic and pollution-free lithium iron phosphate, graphite, organic electrolyte. And at the same capacity, the lithium iron phosphate battery (LFP) is light in weight, and the battery pack of the same specification is about 1/4 of the battery.
Locomotive Battery Management System (BMS)
Due to the increasing complexity of battery technology, especially in lithium-ion systems, battery management systems (BMS) have become critical.
· Real-time monitoring: BMS continuously monitors the voltage, temperature and charging status of the battery to ensure that each battery unit is operating within a safe range.
· Balanced charging: By balancing the power of the battery unit, ensure that all units are charged and discharged at the same rate, thus extending the service life of the battery.
· Safety protection: BMS prevents overcharge, overdischarge, short circuit and overheating, etc., to ensure the safe operation of the battery.
· Data recording and analysis: The system collects battery running data to provide basis for subsequent analysis and maintenance, and optimize battery usage and performance.
· Communication function: BMS can communicate with other systems (such as the locomotive control system) to transmit battery status information in real time, which is convenient for overall monitoring and management.
Locomotive battery charging system
In order for the battery to perform its function effectively, it must be ensured that the battery is always maintained at a high level. The locomotive uses two main technologies to charge the battery, which are also applicable to diesel-electric locomotives:
Vehicle charging system: In terms of on-board charging systems, diesel engines are often used as power sources. It drives a generator that charges the locomotive battery during its use, ensuring it is always ready to provide backup power or support auxiliary operations. For example, one locomotive battery that has attracted public attention is the locomotive battery charger.
External charging infrastructure: Locomotives have the option of connecting to an external charging station at a specified terminal or garage. There are many benefits to this approach, such as: Improved charging efficiency, External charging stations provide standardized and efficient charging procedures, especially during extended periods when the locomotive is not in operation; Reduced emissions: By eliminating the need to run the engine just to charge the battery, this approach promotes a more environmentally friendly operation.
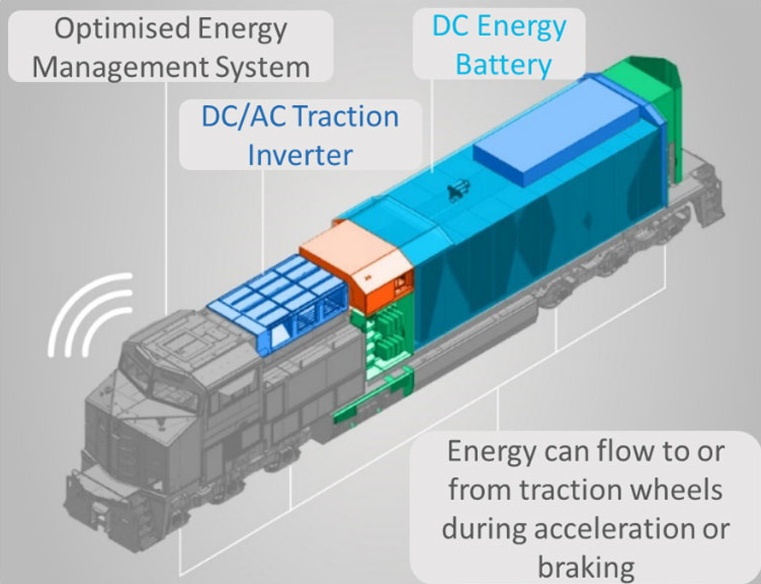
The important role of locomotive battery
Locomotive batteries are not only the key to starting a diesel engine, but also a vital but often overlooked energy storage system. It supports a variety of critical functions, seamlessly powering basic operations. This includes the operation of control systems, lighting, communication equipment and security mechanisms. By ensuring a stable and reliable power supply, the locomotive battery lays the foundation for the seamless performance of these systems. In addition, its capacity and voltage (often measured in terms of the locomotive battery voltage) are critical to maintaining the operational integrity and efficiency of the locomotive's electrical system.
Conclusion
The locomotive battery has evolved from a neglected component to an indispensable component of the locomotive, as the reliability and efficiency of the battery directly affects the operational integrity and sustainability of the railway system. Exploring the application technology of locomotive battery is not only important for improving the performance of locomotive, but also conducive to ensuring the stable and safe operation of locomotive. It also has long-term implications for improving the overall sustainability and efficiency of the rail network.