A Comprehensive Guide to What you Need to Know About Battery Charging Rates
Batteries are very widely used in our daily life, and there are a variety of battery models. However, the C-ratio may be an important concept to understand when using a battery, because the C-ratio of a battery is very important in selecting the appropriate battery to meet the power requirements of a specific application.
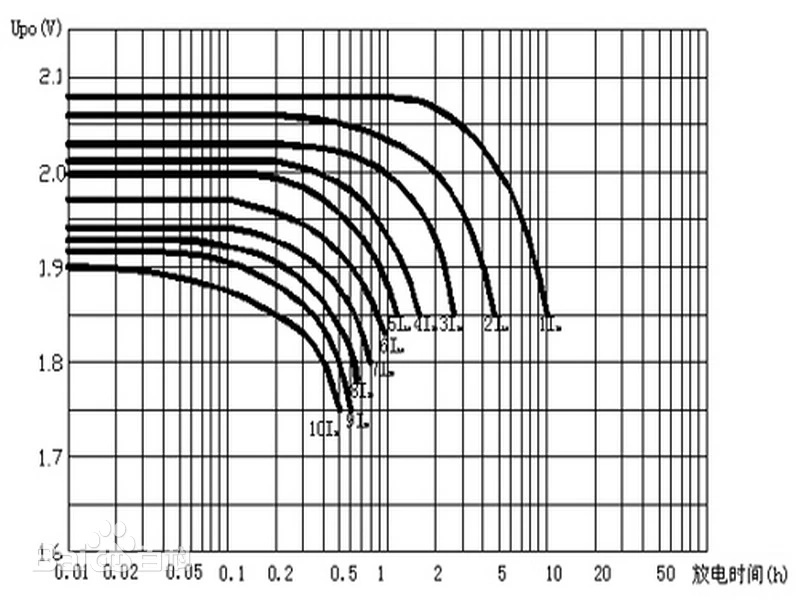
※ Battery discharge rate C function diagram
In general, high C rate batteries are suitable for applications requiring instantaneous high power output, while low C rate batteries are suitable for applications requiring long-term power supply. In addition, when using the battery, it is also necessary to consider the impact of charging and discharging rates on the life and performance of the battery.
Battery C ratio measures the speed at which a battery can be charged or discharged and is expressed as a multiple of the nominal capacity of the battery. Typically, nominal capacity is measured in mAh(milliampere-hour) or AH(ampere-hour) units.
In effect, the C-ratio gives the rate at which a battery can discharge relative to its maximum capacity. The 1C ratio means that the entire battery is discharged in 1 hour, regardless of its capacity.
For a battery with a capacity of 10Ah, 1C is equivalent to a discharge current of 10 amps. For a battery with a capacity of 1Ah, discharge at a rate of 1C, that is, discharge current 1A. Under these two estrus, the discharge time is the same, that is, 1 hour, in 4/1p cases.
If the above battery is discharged at 2C rate, it is discharged within 30 minutes. At 4C, they take 15 minutes to discharge, and so on. Of course, the battery can also discharge less than 1C. At C/2, the battery will discharge within 2 hours. At the C/4 rate, it takes 4 hours, and so on.
C Rating | Time |
30C | 2 mins |
20C | 3 Mins |
10C | 6 Mins |
5C | 12 Mins |
20C | 30 Mins |
1C | 1 Hour |
0.5C or c/2 | 2 hours |
0.2C or c/5 | 5 Hours |
0.1C or c/10 | 10 Hours |
0.05C or C/20 | 20 Hours |
At present, the range of lithium-ion battery discharge rate is below 120C, and the required discharge rate battery can be customized according to the actual demand in the range. That is to say, the discharge rate of lithium-ion batteries has two categories: the rate of 1C to 120C and the small current below 1C.
The charge and discharge ratio of a lithium-ion battery determines how fast a certain amount of energy can be stored into the battery, or how fast the energy inside the battery can be released. The charge and discharge rate performance of lithium-ion batteries is directly related to the migration ability of lithium ions in the positive and negative electrodes, electrolyte, and the interface between them, and all factors affecting the migration speed of lithium ions (these influencing factors can also be equivalent to the internal resistance of the battery) will affect the charge and discharge rate performance of lithium-ion batteries.
Lithium-ion battery according to the different rate, the application of the product is also different, the high rate of lithium-ion battery is related to the ordinary rate, representing the charge and discharge capacity of lithium-ion polymer battery. If the ordinary battery is charged quickly, it is easy to cause the negative electrode to analyze the lithium, resulting in the acceleration of the performance attenuation of the lithium-ion battery, which can cause the internal short circuit of the battery and the fire and explosion.

