Lithium Rechargeable Batteries vs Alkaline batteries,What's the difference?

Lithium Rechargeable Batteries vs Alkaline batteries Basic concepts and meanings
Lithium battery
A rechargeable lithium battery, also known as a lithium-ion battery, is a rechargeable battery that stores and releases energy through the reversible insertion of lithium ions. It is a battery that uses lithium or lithium compounds as its electrode material. It can be divided into lithium-ion batteries lithium polymer batteries and other types. Lithium batteries, with their high energy density, long life, and low self-discharge rate, have become an important power source in portable electronic devices, electric vehicles, and energy storage systems.
Lithium-ion batteries: Use liquid electrolytes and have a high energy density, widely used in mobile phones, laptops, and electric cars.
Lithium polymer batteries: Use solid electrolytes for greater safety and flexibility for thinner and lighter devices.
Alkaline battery
An alkaline battery is a battery that uses zinc and manganese dioxide as electrode materials, and its electrolyte is potassium hydroxide. Due to their low cost and good stability, alkaline batteries are widely used in a variety of disposable low-power devices, such as remote controls, flashlights, and clocks.
Chemical principle and structure
Lithium battery
The basic working principle of a lithium battery involves the insertion and disengagement of lithium ions. When charged, lithium ions are released from the positive electrode (such as lithium cobaltate) and move through the electrolyte to the negative electrode (such as graphite). When discharged, lithium ions are released from the negative electrode back to the positive electrode, and electrical energy is released in the process. Lithium batteries have high energy density and long charge and discharge cycles.
Cathode materials: such as lithium cobalt oxide, and lithium iron phosphate.
Anode materials: such as graphite, and silicon.
Electrolyte: Usually a liquid or solid solution of lithium salts.
Alkaline battery
Alkaline batteries use a chemical reaction between zinc (the negative electrode) and manganese dioxide (the positive electrode) to produce electricity. The electrolyte is potassium hydroxide (alkaline), which can improve the conductivity of the battery and thus improve the performance of the battery. In the discharge process of alkaline batteries, zinc reacts with potassium hydroxide to produce zinc oxide and water, and manganese dioxide reacts with water to produce an electric current.
Anode material: manganese dioxide.
Anode material: Zinc.
Electrolyte: Potassium hydroxide.
Why we should choose lithium batteries instead of alkaline batteries?
Longer service life
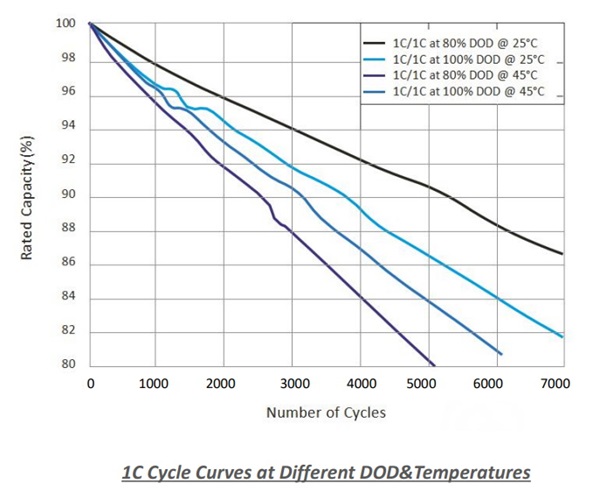
Compared with alkaline batteries, the main advantage of lithium batteries is longer service life. Lithium batteries, on the other hand, are rechargeable, which means they can continue to be charged/discharged to a full charge state. This is achieved by the current flowing through its circuit in the opposite direction to that in which the current flows during discharge.
Lighter weight
Lithium batteries are much lighter than alkaline batteries. This feature gives it an advantage in applications in devices such as power tools, portable wearables and electric vehicles. They also have a longer service life, which makes them widely used in high-tech smart devices and electronic devices.
Cost saving
As I mentioned above, because alkaline batteries are mostly disposable and use cheap materials, they cost significantly less than lithium batteries.
The price of lithium batteries maybe 5 times higher than alkaline batteries, but the service life of lithium batteries is 8 or even 10 cycles longer than alkaline batteries. In addition, lithium batteries maintain almost full voltage at the end of their charging life, while alkaline batteries reduce their voltage output throughout their use. In this way, the cost per use is obviously more cost-effective for lithium ions.
Environmental protection
Alkaline batteries are disposable batteries, which means they are disposable. It is not easy to charge after one use and will be discarded after complete discharge. Therefore, once they are fully discharged, we have to replace them. Lithium batteries are rechargeable lithium batteries that can be recycled. More than 90% of the raw materials are recyclable, so lithium batteries are also environmentally friendly.
In essence, lithium batteries and alkaline batteries are made of different materials and have different structures. This affects their performance in a variety of uses. Alkaline manganese dioxide batteries (commonly referred to as alkaline batteries) are versatile batteries for everyday electronic devices that last longer than other types of batteries. However, lithium iron disulfide batteries (or lithium batteries) have several distinct advantages over alkaline batteries:
Lithium batteries are designed to last longer and are ideal for high-tech, smart devices and electronic devices where battery replacement is inconvenient. They can withstand extremely low temperatures and therefore work well in cold climates. This makes them ideal for outdoor applications. They are lighter than alkaline batteries, making them an advantage when used with portable devices, especially cordless power tools.
In short, in many cases, we can use lithium batteries as a high-performance alternative to standard alkaline batteries. However, the benefits come at a cost: lithium batteries are a more expensive technology, which means a higher price point. These batteries can last longer than the normal life of even some inexpensive, non-critical devices such as toys, so the additional cost may not be justified in each case. In addition, some airlines limit lithium batteries to carry-on travel items.

